Troubleshooting Python Deploys
If your Python app fails to deploy on Render, see below for common causes and resolutions.
For more general-purpose troubleshooting tips, see Troubleshooting Your Deploy.
Incorrect runtime
While creating a Render service, you select the runtime that corresponds to your language:
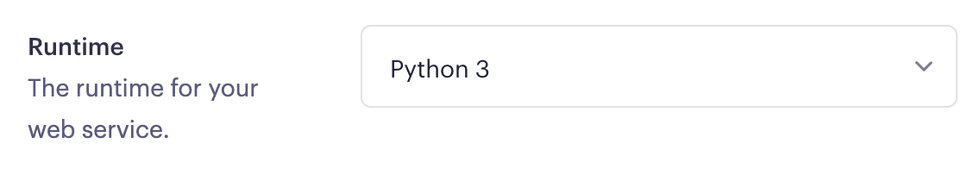
If you select an incorrect runtime, your service’s environment lacks Python-specific tools and libraries that you might need (such as Poetry).
Example symptoms
If you encounter any of the following issues, your service might be using an incorrect runtime:
- Setting the
PYTHON_VERSIONenvironment variable does not change your service’s Python version. - Your deploy logs include messages such as:
bash: poetry: command not found— Poetry and other Python tools are included only in the Python runtime.
Steps to resolve
-
In the Render Dashboard, open your service’s settings and confirm at the top of the page that the runtime is Python 3 (or Docker if your Python app is built from a Dockerfile):

-
If you’re using an incorrect runtime, the fastest fix is usually to create a new service with the correct runtime.
- You can also change an existing service’s runtime via Render Blueprints or the API. See details.
Incompatible Python version
You can set a Python version for your service via the PYTHON_VERSION environment variable:
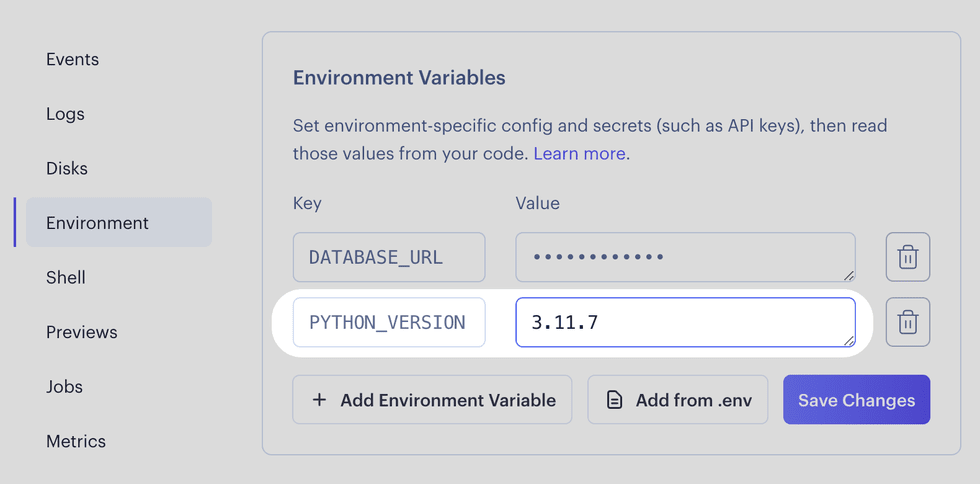
If you don’t do this, Render uses its default version.
It’s possible that your app uses a language feature or a dependency that requires a different version of Python from what your service currently uses.
Example symptoms
If you encounter any of the following issues, your service’s Python version might be incompatible with your app:
- Your deploy logs include messages such as:
Current Python version (3.11.10) is not allowed by the project (^3.12).SyntaxError: invalid syntax.— This often means your code uses syntax that was introduced in a newer version of Python than what your service uses.
Steps to resolve
-
Verify which version(s) of Python your app is compatible with:
- If your project uses a
pyproject.tomlfile, thepythonkey specifies Python version compatibility. - If your app works on your local machine, check which Python version you’re running locally. (If you’re using a virtual environment, make sure to check the Python version for that environment.)
- If your project uses a
-
In the Render Dashboard, go to your service’s Environment page and set a compatible Python version via the
PYTHON_VERSIONenvironment variable:
Missing dependencies
If your app uses third-party libraries (such as packages available on PyPI), you need to install those dependencies in your service’s runtime.
Example symptoms
If you encounter any of the following issues, your service might be missing third-party dependencies required by your app:
- Your app crashes deterministically. It might crash on startup, or when you trigger a specific code path.
- Your deploy logs include messages such as:
ModuleNotFoundErrorImportError
Steps to resolve
-
Specify your app’s Python dependencies in a dependency file. Add this file to your codebase and commit it via version control.
Exactly how you do this differs based on which package management tool you’re using. For example:
- If you’re using pip, commit a
requirements.txtfile. You can usepip freezeto generate this file. - If you’re using Poetry, commit both your project’s
pyproject.tomlfile and the autogeneratedpoetry.lockfile.
- If you’re using pip, commit a
-
In the Render Dashboard, go to your service’s Settings page and ensure that you’ve configured the Build Command to install your Python dependencies.
The command you use depends on your package management tool:
- If you’re using pip, use
pip install -r requirements.txt. - If you’re using Poetry, use
poetry install.
Your build command can run the corresponding command directly (possibly in conjunction with other commands relevant to your build step), or it can execute a script in your repo that includes the command. Learn more about the build command.
- If you’re using pip, use